Plant Containers for Restoration Dee Pots |
|||||||
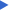
Size and Description Recently, a taller version of the Dee pot was introduced. It has the same diameter and uses the same rack as the standard Dee pots, but is almost twice as tall. The standard dee pots are referred to as D40's and the new, larger containers are referred to as D60's. The vast majority of Dee pots in use are the D40's. Growing Conditions in Dee Pots The shape of the pot can pose some challenges to the grower. Because the container is long and constricted, that there may be periods when the soil is poorly aerated and waterlogged. The shape also makes it difficult to rehydrate a dried out plant. Often, we water plants, believing that we are keeping the soil fully hydrated. Later, when we take the plants out of the pot, we find that most of the soil mass is dried out. |
 |
||||||
The following plants are commonly grown in dee pots: Trees, except for those with thick taproots, such as buckeye (Aesculus californica) In sum, plants grown in Dee pots should be adaptable to occasional waterlogging as well as occasional drying out. Advantages of Dee Pots 1. The containers are narrow, so that many plants can be grown in a small amount of space. Problems and Disadvantages Because the containers have a small surface area, it is more difficult to keep them properly watered. This is easily accomplished in a nursery, where we have a regular watering schedule. However, it requires more diligence in the field to keep them hydrated. One of the main advantages of the dee pot is that the roots are placed deeply in the soil, however, this can be a problem during installation , particularly if the planting site is hard or rocky. There is a temptation to cut corners by shoving the roots into a shallow hole or to lay part of the rootball sideways. Ideally, the hole should be deep enough so that the entire rootball is installed completely vertically. If the hole cannot be dug deep enough, it is best to cut off the bottom of the rootball, so that the remainder is installed correctly. |
 |
||||||
 |
|||||||

Back to Restoration Containers